This post was originally published on harperdb.io
Recently “the cloud” has become a vital part of technology, and Cloud Engineering jobs have been brought to the limelight. Cloud technologies have greatly influenced how we interact with computers both for work and play. The good news is, you don’t have to have a degree in computer science to understand the Cloud. In this article, you will learn about Cloud Engineering and why this part of tech has become very important in how we think about innovation today.
A Quick Backstory – Before The Cloud
Before cloud computing, there was client/server computing, a centralized location where all software, data, and control lived on the server side.
If a user wanted data or any other form of access, they could connect to the server, get access, and do work. Later, distributed computers came into existence. In this model, all computers are connected through a network. This set the footprints for the implementation of cloud computing, which came later.
In a speech at MIT around 1961, John McCarthy proposed that computers could be sold as utilities like electricity. It was a fantastic idea, but like all awesome ideas, it was ahead of its time. Because despite the interest, the technology is not ready for it in the coming decades.
Decades later, companies like Salesforce, Amazon and Microsoft implemented cloud computing technologies and other organizations followed suit.
What Is The Cloud?
A lot of people say the Cloud is someone else’s computer, but in my opinion, this definition should include a lot more. So what does “the cloud” really mean?
The cloud is a collection of computing resources — databases, servers, storage, applications, networking capabilities, and more — hosted at a distant data center and operated by a cloud services provider. The provider makes these resources available for a subscription fee or bills them by use.
What Is Cloud Engineering
Now that you know what the cloud means, the concept of Cloud Engineering should make more practical sense. Cloud Engineering is engineering in the context of the cloud. It leverages the methods and tools of engineering in designing, building, operating and maintaining cloud services. Often, Cloud Architects, Cloud Engineers, and/or Solutions Architects are in charge of connecting complex business problems with the proper cloud solutions through solution architecture and design.
Importance of Cloud Engineering
In recent times, many organizations have embraced and hired for more Cloud Engineering roles. This is because of the importance of the cloud in technology and innovation in general. Cloud Engineering helps organizations achieve the following:
- Scaling up or down: Cloud computing allows you to use the exact number of resources you need. Thus, depending on your business requirements, you can increase or decrease your infrastructure investment.
- Continuous Integration & Deployment: One of the benefits of cloud computing is the automation of code builds, testing, and deployments. These benefits have made teams deploy and rollback features quicker than ever.
- Cost: Companies pay only for resources they use, making cloud computing a better economical option than managing their resources. Companies also do not have to invest in expensive hardware, storage devices, software, etc.
- Disaster Recovery: Because all data is stored in the cloud, backup and recovery are quicker and more reliable.
- Security: There is double protection because the cloud service provider and the organization (customer) make the cloud application security compliant.
- Flexibility: Depending on your business needs, different services can help you solve your specific problem.
Traditional Cloud Service Models
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a self-service model for managing infrastructure in data centers. Organizations pay for IaaS on a subscription as opposed to buying physical hardware. This model enables companies to add, delete, or reconfigure IT infrastructure on-demand.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) makes it more straightforward and quicker to develop, test, and deploy applications.
Developers can focus on writing code and building applications without worrying about time-consuming infrastructure activities like provisioning servers, storage, and backup.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a service (SaaS) substitutes the traditional on-device applications with applications hosted in the cloud. SaaS applications can be accessed directly from a web browser and they don’t require any downloads or installations.
Newer Cloud Service Models
Cloud service models are beyond IaaS, PaaS and SaaS. There are other ways that computing services are provided on the cloud and some of them are listed below:
- Security as a Service (SEaaS)
- Storage as a service (STaaS)
- Backup as a service (BaaS)
- Network as a service (NaaS)
- Database as a service (DBaaS)
In this article, we will touch on Database as a Service.
Database As A Service
Database as a Service (DBaaS) is a cloud service model that allows users to access a database system on the cloud without buying and setting up their hardware, installing their database software, or managing the database themselves. The cloud provider handles periodic upgrades, backups, availability and security.
Using HarperDB On The Cloud
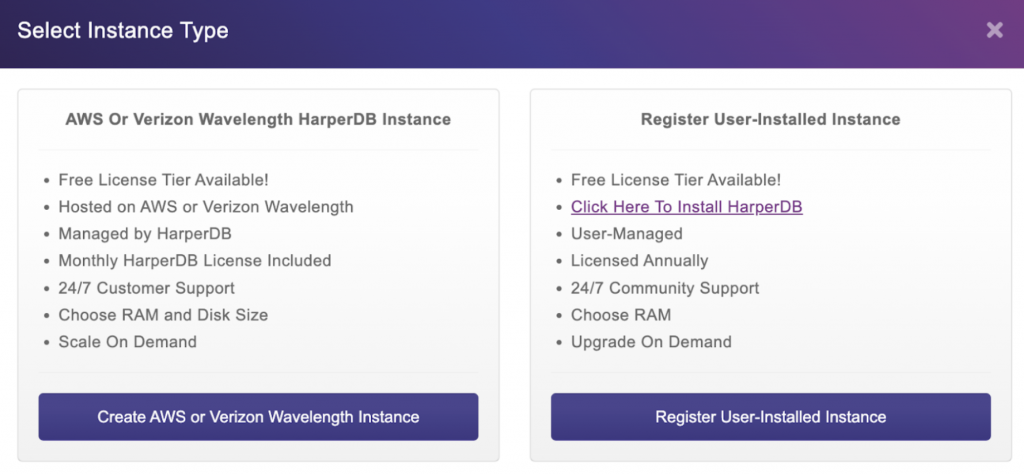
HarperDB has a cloud offering that could be considered a DBaaS, PaaS, or SaaS. It handles the deployment and management of your instances in just a few clicks. Currently you can spin up either an AWS (Amazon Web Services) instance or a Verizon Wavelength instance through the HarperDB Studio:
HarperDB can run on anything with an operating system, and saves valuable resources by removing the need to set up and manage database systems and the IT environment. Other advantages of HarperDB Cloud are listed below:
Advantages of HarperDB Cloud
- Resource elasticity: The technology resources dedicated to database systems can be changed in response to changing user requirements.
- Rapid provisioning: You can provision new database instances as required, with a few simple clicks. This removes the governance hurdles and administrative responsibilities from IT.
- Security: HarperDB implements user roles and access levels, so only authorized users gain access to data.
- Other Features: Other notable features of HarperDB include a built-In HTTP API, scalable performance, Custom Functions, and seamless developer experience.
Conclusion
In this article, you learned about Cloud Engineering and its importance in our industry today. You were also introduced to traditional cloud service models and some new cloud models, including Database as a Service (DBaaS).
One example of a DBaaS solution is HarperDB Cloud, which you can use within the HarperDB studio. Sign up to HarperDB cloud to get started and get a free instance forever.
